Browsing with Google Chrome
Browsing with Google Chrome

What's coming up?
In this activity you'll find out about the Google Chrome web browser, and how to use it to help browse the web more safely and conveniently.
This activity is about Google Chrome on desktop and laptop computers, but if you use Chrome on your mobile device, you should still be able to follow along.
Start activityWhat is Google Chrome?
Google Chrome - usually just called Chrome - is a free web browser created by Google.
Chrome is provided by default on Android devices.
For all other devices, it can be downloaded and used for web browsing, regardless of brand or device type.


How to get Chrome
Chrome can be used on any device, regardless of brand. Even if you already have a different web browser installed, you can still download and use Chrome if you prefer.
For Windows devices, you can install Chrome from the Microsoft Store.
For Apple devices, you can download and install Chrome from the App Store.
You can also get Chrome from chrome.google.com.

eSafety tip
The first time you use Chrome, you may be asked to confirm if you want to have Chrome as your default browser. Agreeing to this means that any links you click on from other programs will open in Chrome, not another browser.
You don't have to say yes unless you are happy to use Chrome as your default, so you can safely decline this request. Chrome may repeat the request intermittently afterwards and it's ok to accept or decline later, depending on your preference.
Chrome keeps itself up to date
It's important that all web browsers stay up to date, to keep on top of known malicious websites and other threats.
Chrome updates itself automatically. Sometimes, it may show you a small button prompting you to Update or restart Chrome to apply the update.
Other times, the update is applied automatically the next time you turn on your computer and open your browser.


Chrome helps you browse privately
Normally, web browsers keep a record of every website you visit in the browser History. If you'd rather browse without having this history recorded, you can use Chrome's Incognito Mode:
- Click the three dots in the top right of the main Chrome panel
- Click New Incognito Window
- A new browser page opens with a black border and an Incognito logo in the corner.
Browsing in Incognito Mode makes it harder for sites to track you and target ads to you, so it's more private.

eSafety tip
When you use Incognito Mode, the sites you visit won't be recorded on your device's browser history, but it's not completely anonymous. Your ISP (Internet Service Provider) and others will still be able to track your internet activity.
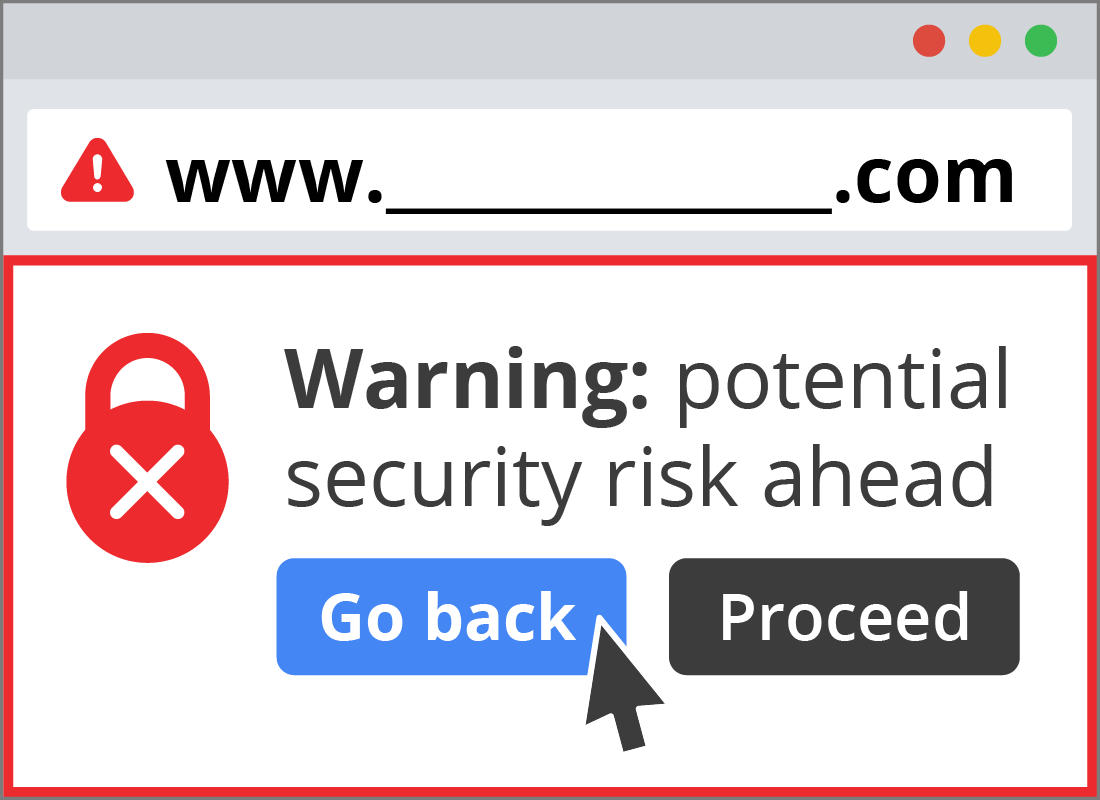
Chrome blocks known malicious websites
Some websites are set up to give devices that visit the site a virus, or to try to steal the identity of people who use the site. These are called phishing sites and Chrome gets updates from Google about these unsafe sites.
If you try to visit a known phishing site, instead of loading the site, Chrome will display a warning message on your screen letting you know that visiting the site is not safe.
You can then press Go back and find a different site to visit.

eSafety tip
Even though Chrome will block most known phishing sites and even some viruses and other malicious software, it's still a good idea to install an antivirus package to help keep your device safe.
You can find out more in our Using antivirus software course.
Signing in to Chrome
You can sign in to Chrome using your Google Account. If you don't have a Google Account, you can create one for free. Our Android phone: set up course shows you how to do this, and the steps are similar on any computer.
When you sign in to Chrome, you get extra features, including a free password manager to keep your passwords safe. You can learn more about password managers in our Managing passwords course.
Cookies in Chrome
Many websites will ask permission to save a cookie on your computer when you first visit. These cookies may be used to personalise the site, or even target you with ads.
From time to time, some websites may stop loading content correctly and deleting cookies might resolve this problem. You may never need to delete cookies, but it's good to know where to find them, just in case.


Deleting cookies in Chrome
To delete cookies that are stored on your computer:
- Click the three dots in the top right of the main Chrome panel
- Choose More Tools
- From the extra menu that opens to the side, choose Clear Browsing Data…
- A panel opens, and you can select Cookies and other site data
- To delete all cookies, click Clear data.
Clearing your browsing history
Every website you visit using Chrome is recorded in Chrome's History. You can manage your privacy by deleting some or all of these records:
- Click the three dots in the top right of the main Chrome panel
- Choose More Tools
- Then choose Clear Browsing Data…
- A panel opens, and you can select the Time range you want to delete
- Select the Browsing history option
- Click Clear data.


eSafety tip
The Clear browsing data panel allows you to choose the Time range for deletions. Options are from the Last hour to All time. Be sure to choose how far back you want to delete before clicking on Clear data.
You can also use this panel to delete cached (saved) images from your browsing data. Your browser saves some images from websites you have visited so that you don't need to reload the image on your next visit. Deleting cached images frees up some storage space on your computer, but next time you visit the site, it might take a little longer to load.
Bookmarking in Chrome
Once you've found the website you're looking for, you can get back to it quickly in the future by using a handy little feature called a bookmark. Bookmarking a web page is just like bookmarking a page in a book - and you can create as many bookmarks as you like for all your favourite websites.
The following panel has a video that shows you how to bookmark a web page using Chrome.

Bookmarking a web page in the Chrome browser
A bookmark creates a handy shortcut to a web page, so you don't have to type its address or search the internet to find it again.
Any web page you visit regularly, or which you want to remember, can be saved as a bookmark in your computer's web browser. Let's look at how to bookmark a web page in the Chrome browser.
First, type the name of the web page you want to open in the Address bar.
With the web page open, click the bookmark icon in the far right of the Address bar. It looks like a star. A drop-down menu will appear with the name of the web page highlighted. You can keep the name suggested by Chrome or type another name into the box if you'd like.
Now, let's choose where to save the bookmark. In the Folder drop-down menu, check that Bookmark bar is selected. Now, click Done.
And that's all there is to it. Next time you want to visit that web page, click on the three vertical dots at the far right of the browser. From the drop-down menu that appears, go to Bookmarks to open the bookmarks menu. Simply click on the one you want to open. It's as easy as that.
Chrome browser extensions
Chrome supports small programs called browser extensions. These aren't standalone apps, but more like extra tools and functions you can add to Chrome.
You can even get an extension that blocks ads. You can find out more about this in the More tips for safer browsing activity later in this course.

Well done!
This is the end of the Browsing with Google Chrome activity. You should now know how to manage cookies and some browser settings to help use Chrome more conveniently, safely and privately.
If Chrome is the only browser you use, you can skip ahead to the More tips for safer browsing activity. Or you can continue to learn about safety tips for Browsing with Microsoft Edge.