General

How to spot fake news online
Being online can sometimes feel like walking through a crowded marketplace - so much noise, distractions, and people calling out for your attention. Instead of great deals on fresh fruit and veg, you’re bombarded with dramatic headlines, intriguing images, and ads competing for your clicks. And in the race to catch your eye, not everyone feels that honesty is the best approach.
Alongside the factual and informative news we see online, there’s fake news. It’s not new. Misinformation and propaganda have existed for centuries, but today fake news spreads faster and wider thanks to the internet and social media.
So how can you tell fact from fiction? In this guide, we take a look at what fake news is, how it spreads online, and share practical tips to help you spot it.
In this article:
- What is fake news?
- How does fake news spread?
- Tips to spot fake news
- AI generated images
- How to spot AI generated images
- Tips to keep you from getting caught by fake news
What is fake news?
Fake news refers to false or misleading stories designed to influence how you think, act, or even vote. It comes in different forms.
Satire. Satirical news is made up for entertainment and meant to be taken as a joke but can be misleading when it’s shared by people who don’t understand its comical nature, or it’s taken out of context. Great examples of satirical news sites include The Betoota Advocate and The Onion .
Clickbait headlines. These are attention grabbing headlines designed to get you to click on them. The problem? The article often has little or nothing to do with the headline. This tactic is known as clickbait. Typical examples include, ‘You won’t believe what Kylie Minogue looks like now!’, or ‘This woman made $550,000 working from home – find out how!’
Disinformation. This is deliberately misleading information created to deceive or confuse people and promote a specific agenda.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) content. AI can create fake content including fake images or videos that can take real people or objects and present them in situations that never happened. Spotting AI generated videos or images can sometimes be tricky, but there are ways to tell when they’re AI generated. More on this later.
How does fake news spread?
Many people now turn to social media for their news, so platforms like Facebook and X (formerly known as Twitter) make it easy to share fake stories. With just a click on Share or Like, a story or image can reach thousands of people and gain traction in a matter of hours. People are also more likely to share stories that confirm what they already think. In times of crisis, people look for information that connects with their emotions, which makes news spread quickly. At such times, accurate and trustworthy information is even more powerful as it helps calm fears and restore confidence.
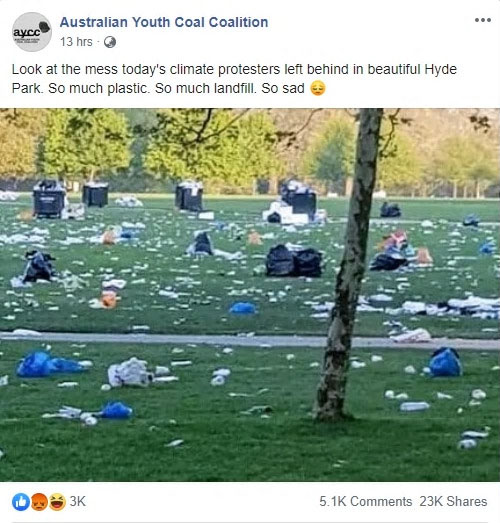
Example of fake news. This Facebook post claimed rubbish was left behind by Sydney protesters, however it later emerged this picture was taken at an unrelated event in Hyde Park, London. Tips to spot fake news
Check the source. Consider how reliable it is. Is it a reputable news organisation, a satirical site, or a Facebook group? Also, consider where you found the article. Treat information from social media with careful consideration.
Check the web address. Some fake news sites use web addresses that look very similar to real news sites. So, check the URL to make sure you’re visiting the right website for your news.
Check the author. Who wrote the piece? Are they credible? Do they have an agenda? An online search can reveal whether they’ve written for reputable news organisations.
Check for evidence. Is the story based on fact or opinion? Who are the author’s sources? If there’s little or no evidence, that’s a red flag the story may be fake.
AI generated images
Artificial intelligence (AI) software can create realistic looking images or videos to spread false information. Deepfakes are a type of this technology where a photo, video or audio is digitally altered to make it appear as though someone said or did something they didn’t. For more information about AI, read our What is AI? article to find out how AI learns, different types of AI, and some of the ways it can help us.
How to spot AI generated images
As AI and deepfake technology becomes more sophisticated, it can be harder to detect when it’s being used. But sometimes there are signs that can help you spot the less advanced fake photos and images.
Hands and fingers. AI has often had trouble with human hands, sometimes giving them too many fingers or merging fingers in strange ways. Checking the hands of people in an image can be a way to spot AI, although this is becoming less effective as AI improves.
Facial details. Pay attention to things like skin tone – does it look too perfect or smooth? If there’s facial hair, does it look unnatural? If the person is wearing glasses, look for jagged edges or strange shadows. And if the person is wearing earrings, check if the left and the right pair look symmetrical.
Signs, logos, and text. AI struggles to accurately recreate signs, logos, and text. If you see a photo or video of an official announcing something that seems suspicious, check for errors like altered logos, misspelled words or wrong mottos.
Details and background objects. AI can sometimes include details that wouldn’t naturally appear in real-life scenes or leave out elements that should be there. Look out for things that don’t make sense contextually, like the corners of a room not lining up. AI also struggles with shadows and lighting, so check for shadows that don’t belong or inconsistent lighting.
Keen to test your AI image spotting skills? Take this quiz to see if you can tell if an image is real or fake.
Tips to keep you from getting caught by fake news
Here are a few tips to protect yourself against being misled by fake news.
- The first step is knowing that fake news is out there and comes in many forms.
- Get your news or information from trustworthy outlets such as major national or state media services or government websites. Try to avoid getting your news from social media outlets.
- Question what you read – does it offer multiple perspectives? Or does it only confirm what you already believe to be true? Try to get your news from a variety of sources.
- Do a reverse image search to help you decide if a photo is fake. If the image appears somewhere else online, you’ll see how other sites have used it and when the photo was taken.
- Check the accuracy or authenticity of a story by doing your own web searches or using fact checking websites such as AAP (Australian Associated Press) FactCheck , FactCheck.org or Snopes.com .
This article was originally published on 23 June, 2020.