How is Wi-Fi different from 4G and 5G?
How is Wi-Fi different from 4G and 5G?

What's coming up?
In this activity, you'll learn the difference between Wi-Fi signals and mobile phone signals, such as 4G or the newer 5G.
Even though both types of signal can be used to connect wirelessly to the internet, 4G and 5G are really meant for when you are on the move.
Start activityWi-Fi range vs 4G/5G
Wi-Fi relies on a router inside your home (or other building, such as a library) to provide a wireless internet connection to your devices.
The router can provide Wi-Fi reception to devices up to 30 metres away, so is great for local use. Wi-Fi is often referred to as the home internet.
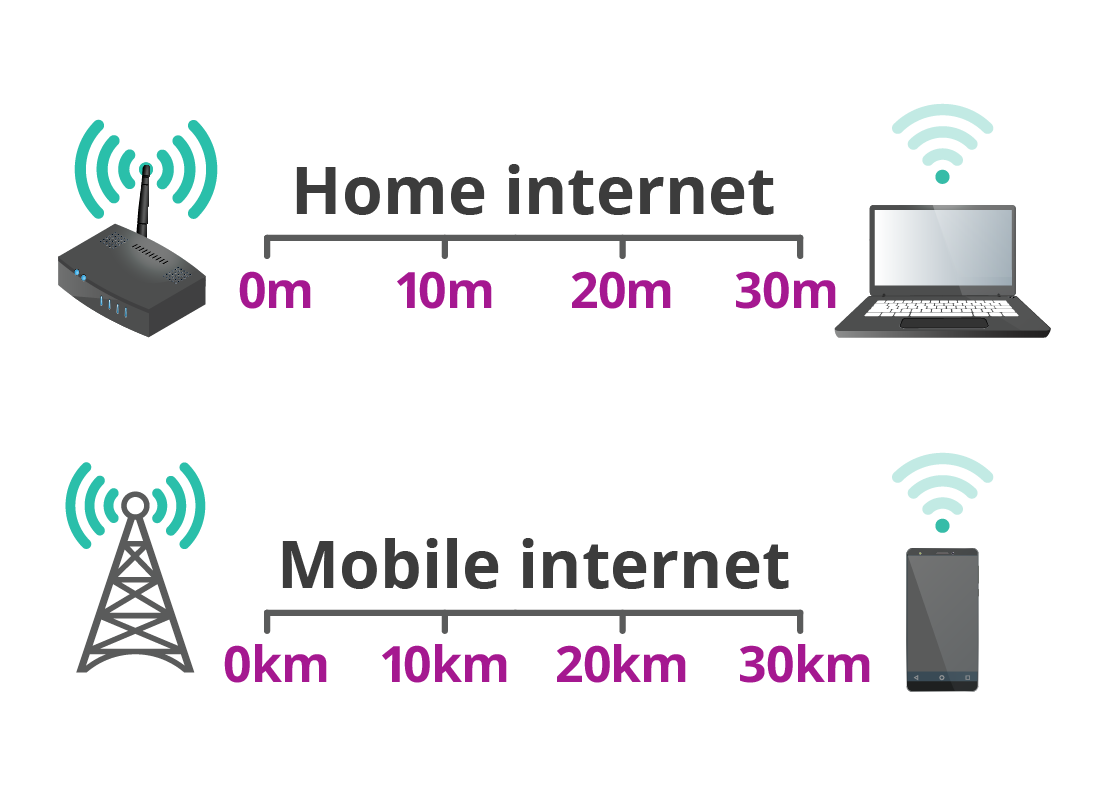

4G/5G range
4G stands for Fourth Generation and 5G stands for Fifth Generation. Each generation offers faster internet access than the previous.
With 4G and 5G, mobile phone towers provide the wireless internet connection to your devices. A tower can provide wireless internet reception to devices many kilometres away, so is ideal for use across wide areas and when you are on the move, such as on a bus or train.
4G and 5G are often referred to as the mobile internet.
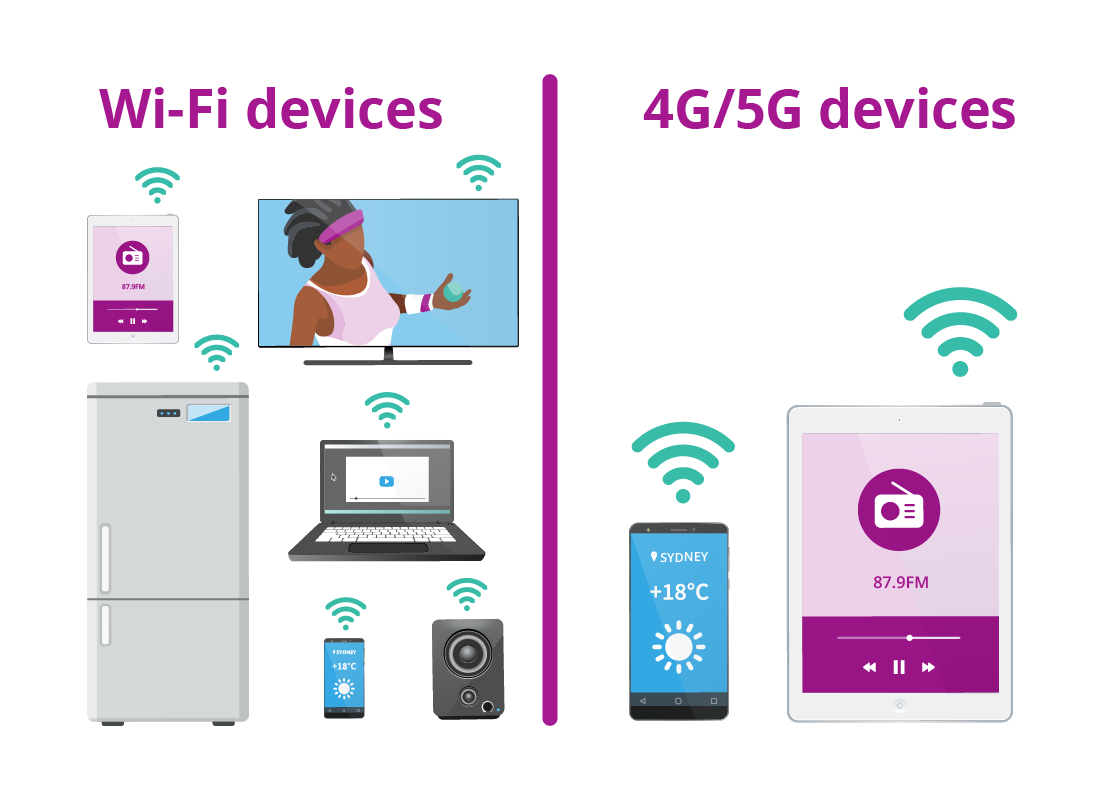
Wi-Fi devices vs 4G/5G devices
Wi-Fi devices include TVs, speakers, fridges, laptop computers, phones and tablets, but 4G and 5G devices are mostly mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets.
For a device to connect to 4G and 5G wireless internet, it needs to be part of a mobile phone account.

The difference between 4G and 5G
Wireless internet technology changes and improves all the time. The same can be said for mobile internet technology. The current fastest and most widely available mobile internet is called fourth generation, or 4G.
Some areas already have access to the newer, faster fifth generation, or 5G, network. However it is not yet available everywhere or on all older devices.
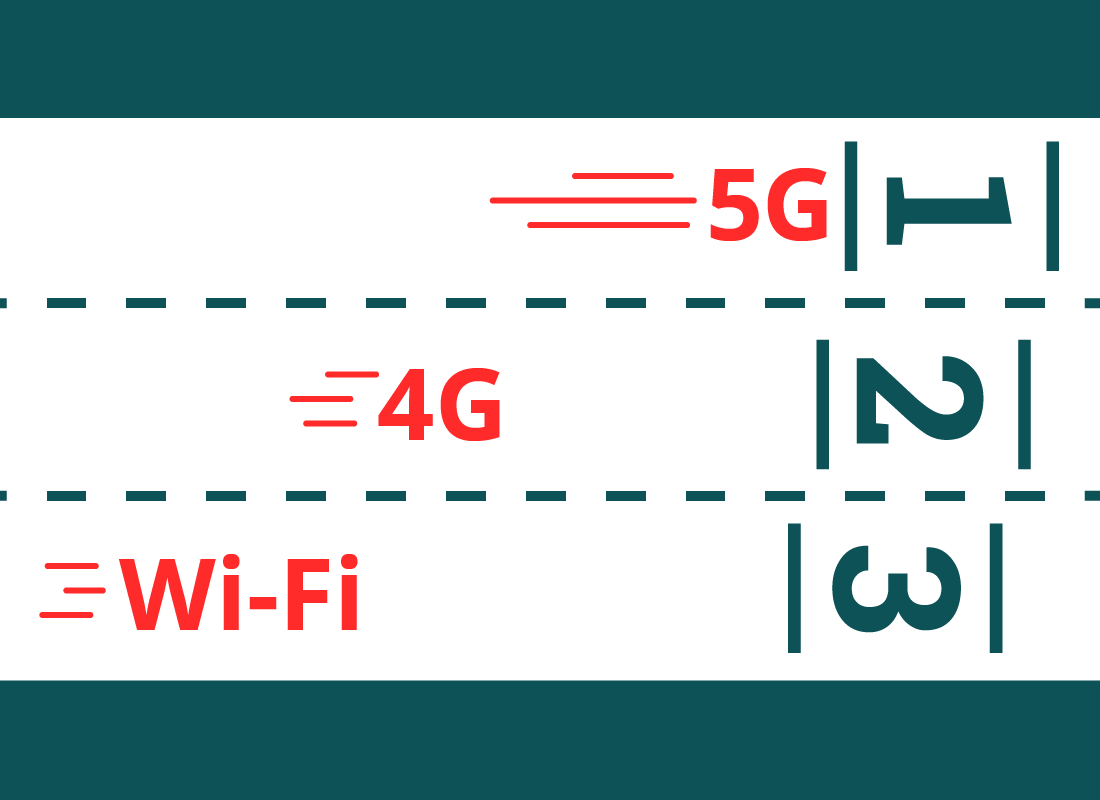
Mobile vs home network speed
A fast, wireless internet connection is a good internet connection. It means less waiting around for web pages to appear or for photos to upload. It also lets multiple people use the internet at once, without interruption.
For most people, 4G mobile internet will be a bit faster than a home Wi-Fi network. 5G will be much faster than most current Wi-Fi networks.

Mobile vs home network costs
The 4G and 5G mobile internet is faster and provides wider reception range than Wi-Fi, so why not use it all the time? You can, of course, but mobile internet is a lot more expensive than home internet.
Everything you read, listen to or look at on the internet is sent to your device as data. Data is measured as gigabytes, or GB for short. A typical home internet data allowance is usually much larger and cheaper (per GB) than a typical mobile data allowance, so using your home Wi-Fi network data whenever possible will be the most economic way to browse the internet.
You can find out more about how data is measured and managed in our All about data topic.
Well done!
You've completed the How is Wi-Fi different from 4G and 5G? activity.
You've learned that Wi-Fi comes from a home internet connection, while 4G and 5G are mobile internet connections.
4G and especially 5G can be faster than a Wi-Fi network, but they are much more expensive.
Next up, if you have registered and are logged into the Be Connected website, you'll now be able to take a short quiz to finish the course. If you're not registered, you are now at the end of the What is Wi-Fi? course.
